Categories
In this article
- What is retention?
- Default Drive data retention in Google Workspace
- How to safeguard Google Drive files using retention rules in Google Vault?
- How to use eDiscovery to safeguard Google Drive files?
- Are Google Vault retention and eDiscovery hold ideal data backup solutions?
A Guide to Google Drive Retention Policy for Businesses
9 Apr 2025
12 min read
Annu Sabu
Google Drive retention at a glance
- Files deleted from Google Drive, whether intentionally or accidentally, can be lost permanently if not recovered within the retention period.
- Google Workspace’s retention rules are often complex and may not cover all scenarios, leaving gaps in data protection.
Read more
Google Drive has become one of the most popular file storage and collaboration services used by organizations worldwide. The number of active users on its site per month amounts to around 2 billion, including most of its users who are accessing productivity tools from Google.
1. What is retention?

2. Default Drive data retention in Google Workspace
For a step-by-step guide to recover deleted Google Drive files from trash, click here.
Note: The default retention is applied to files in both Drive and Shared Drive.
To know how a Google Workspace Administrator can recover permanently deleted files from Google Admin Console, click here.
Limitations of default data retention in Google Workspace for Google Drive
- Files retained under Google’s default retention policy (such as items in the Trash) continue to count against your Google Workspace storage quota until they are permanently deleted. If your organization exceeds its pooled storage limit, additional storage may need to be purchased.
- Data is automatically deleted forever once the default retention period expires after 30-55 days.
3. Native data retention settings in Google Workspace to safeguard Google Drive files
- Retain organizational data indefinitely or for a certain time period
- Automatically delete organizational data after a certain time
- Hold, search, and export organizational data for eDiscovery
To know more about what Google Vault is, Vault retention rules, holds, and license requirements, read our in-depth article on Google Vault Fundamentals.
3.1 What Google Drive data can be retained using Google Vault?
| Items within the scope of retention | Items outside the scope of retention |
|---|---|
Google Docs | Linked files |
Google Sheets | ‘Shared with you’ files from external users |
Google Slides | |
Google Forms | |
New Google Sites | |
Google Drawings | |
Google Meet recordings & associated chat | |
Q&A and Polls logs | |
Jamboard files in users’ Drives | |
Non-Google files uploaded to Drive | |
Files in Shared Drive | |
What are linked files?
3.2 How to safeguard Google Drive files using retention rules in Google Vault?
- Default retention rules
- Custom retention rules
3.2.1 Default retention rules
Note: Organizations can apply a default rule apply only if a custom rule or a hold is not already in place.
Create a default retention rule for Google Drive
Step 1: Log into Google Vault.
Step 2: Click on ‘Retention’
Step 3: Select ‘Drive’ from the list of services
Step 4: Choose the retention period for the files
- Choose the retention period
- Enter the number of days
- Choose the reference time for the beginning of the retention period
Step 5: If you have set a retention period, then choose what happens to the files after the retention time expires.
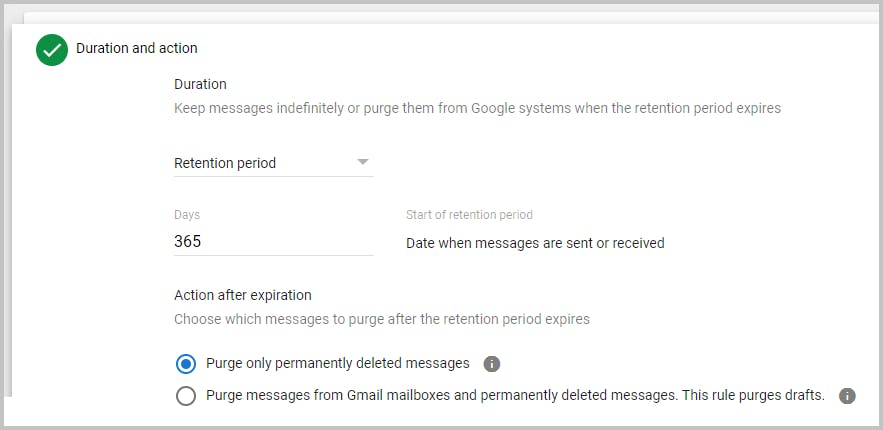
Step 6: Click Create. If you have set a retention period Vault will ask you to confirm that you understand the rule's effects. Check the boxes and click ‘Accept’ to create the rule.
Note: Once you set a retention period, Vault will immediately delete files that exceed the retention period when you create the retention rule. If not configured properly this may delete data that was not meant to be purged.
3.2.2 Custom retention rules
Note: Custom retention rules always take precedence over default retention rules for that service.
Define a custom retention rule for Google Drive
Step 1: Log into Google Vault.
Step 2: Navigate to Retention > Custom Rules > Create
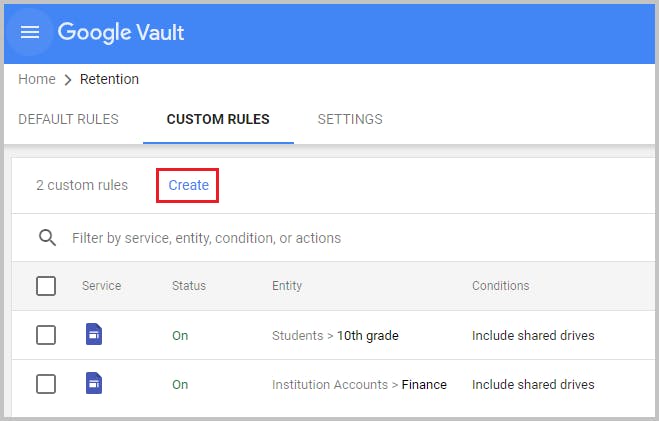
Step 3: Under service select Drive and click on Continue.
Step 4: Choose the entity that you want to apply the rule to.
To apply to a Specific Organization unit: - Select the option and choose the Organizational unit. To learn more about retaining data at an organizational unit level, click here. - (Optional) Select the option ‘Include results from shared drives to apply the rules to all the shared drives the accounts in the selected OU are members of.
- To apply to all Shared drives, select the ‘All shared drives’ option
- To apply to a shared drive that a specific account is a member of: - Type in the account names and click ‘Find’ - Select the shared drives you want the rule to apply to - Click ‘Add’
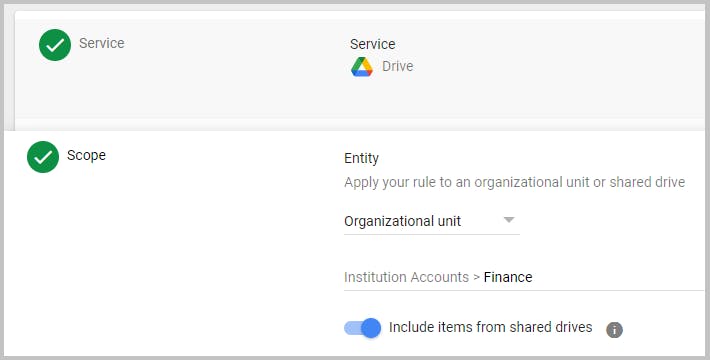
Step 5: Click Continue
Step 6: Define the retention time period. Select the option ‘Indefinitely’ to retain files forever.
To automatically delete files after a certain time:- Choose the retention period
- Enter the number of days
- Choose the reference time for the beginning of the retention period
Step 7: If you have set a retention period, then choose what happens to the files after the retention time expires.
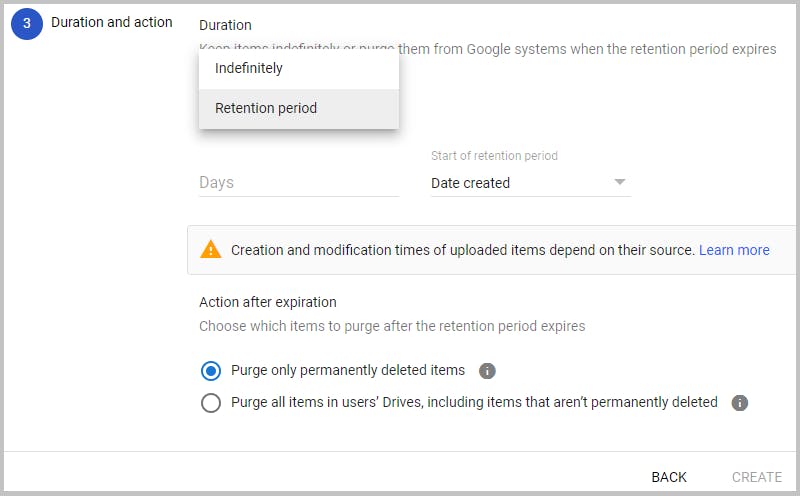
Step 8: Click Create. If you have set a retention period Vault will ask you to confirm that you understand the rule's effects. Check the boxes and click ‘Accept’ to create the rule.
Note: Once you set a retention period, Vault will immediately delete files that exceed the retention period when you create the retention rule. If not configured properly this may delete data that was not meant to be purged.
3.3 What happens when a Google Drive that is covered by a retention rule gets deleted?
Retention rule behavior and conflicts
- Custom drive retention rules in Google Vault can only be applied to files with unique upload/last modified date or among unique users.
- If there was a clash between two retention rules where the files have the same create/last-modified date, Vault will only consider the rule that was created first.
3.4 How does retention work for apps that store data in Google Drive?
Jamboard jams and Google Meet recording are by default governed by the Drive retention settings. If you want to retain Meet recording different from the Drive settings, then you can turn on separate retention for Google Meet recordings and this will supersede the Drive retention settings.
Sites are by default covered by the Sites Retention rule. If you want them to be retained the same way as your Google Drive, you can change the Sites retention settings.
3.5 How to use eDiscovery to safeguard Google Drive files?
To learn how to place your Drive data on hold, read our article ‘Google Vault Fundamentals’.
Note: Hold can be applied only to items created by members of your organization and not to those created and shared by external users.
3.5.1 What all does a hold cover in Google Drive?
| Items covered by hold | Items not covered by hold |
|---|---|
Items created by users | Drive folders |
Items directly shared with users | Drive Shortcuts |
Items in shared drive directly shared with a user | Items owned and shared by external users |
Note: Shared Drives cannot be directly put on hold. To put a shared drive on hold, you must put its members on hold and check the Include shared drives option.
3.5.2 What happens when an item on hold is deleted?
3.5.3 What happens to a deleted shared drive item that was on hold?
To learn how to apply a hold to Google Drive data, read our in-depth article, Google Vault Fundamentals.
4. Are Google Vault retention and eDiscovery hold ideal data backup solutions?
Google Vault is not a backup solution
Vault is built for compliance, not recovery
To learn more about why retention is not backup, read our in-depth article, “Google Vault’s eDiscovery and Retention Rule vs. SysCloud’s Backup for Google Workspace”.
Third-party cloud backup solutions like SysCloud are a one-stop solution to your data backup and restore problems.
Back up Google Drive data with SysCloud
Discover how SysCloud enables comprehensive backup, unlimited retention, and seamless restoration of Google Drive data and other Google Workspace services.
Recommended content
9 Apr 2025
12 min read
6 Dec 2021
5 min read
8 Dec 2021
12 min read
15 Nov 2024
6 min read
Get actionable SaaS administration insights
We don’t spam. Unsubscribe anytime.
In this article
- What is retention?
- Default Drive data retention in Google Workspace
- How to safeguard Google Drive files using retention rules in Google Vault?
- How to use eDiscovery to safeguard Google Drive files?
- Are Google Vault retention and eDiscovery hold ideal data backup solutions?

