Categories
In this article
- What is Gmail data retention?
- Default Gmail retention in Google Workspace
- Native Gmail retention settings
- Are retention rules and ediscovery an alternative to cloud backup?
A Guide to Data Retention in Gmail
6 Dec 2021
6 min read
Gopika
With over 5 million business users, Gmail has grown to become Google’s most successful product yet and one of the most popular email clients globally.
1. What is Gmail data retention?
1. 1. Default Gmail retention in Google Workspace
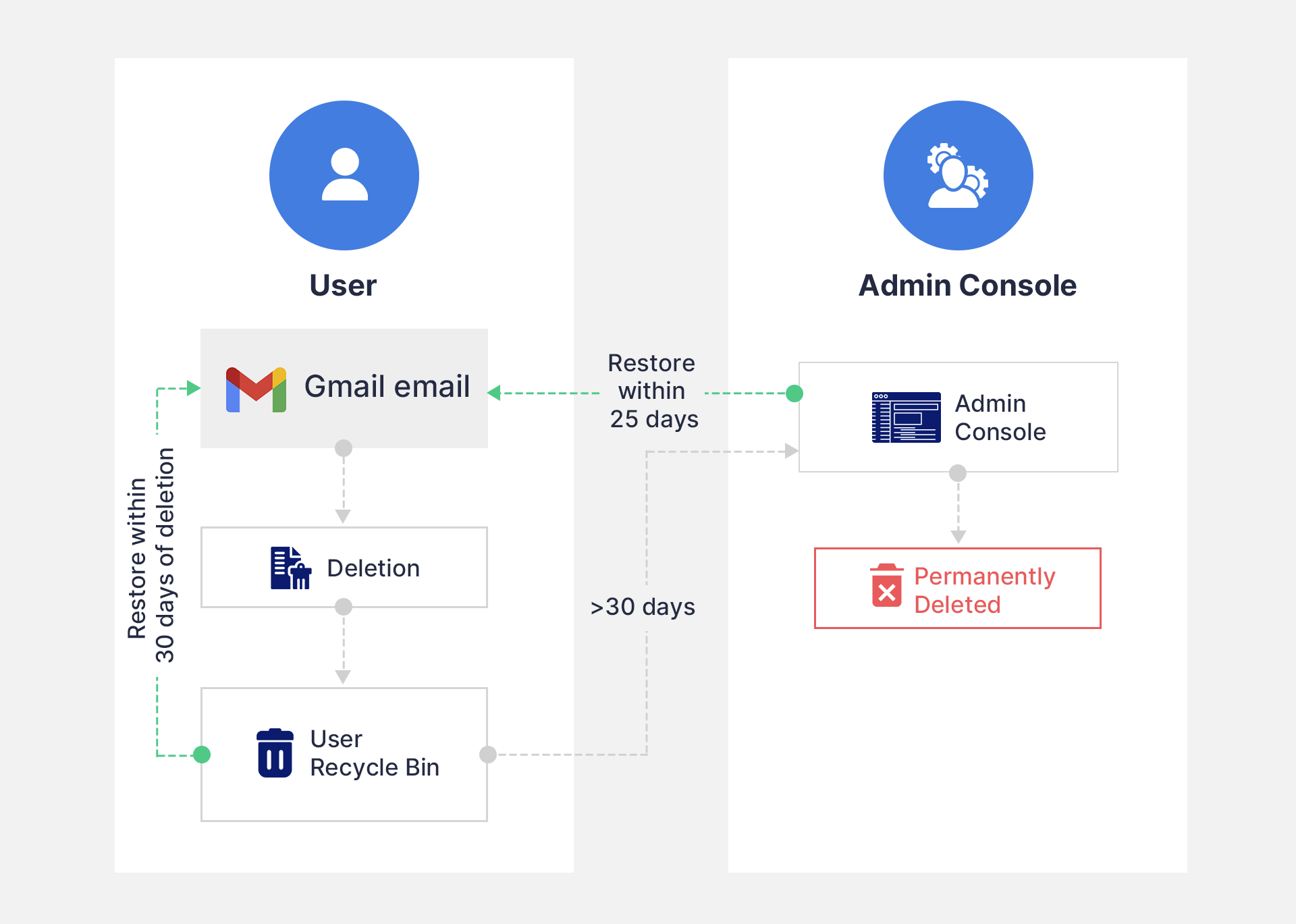
For different ways to recover Gmail emails, click here.
Limitations of default Gmail retention
1.2. Native retention settings to secure Gmail
Google Workspace also offers native retention settings in Google Vault to help organizations retain Gmail emails efficiently, and for a longer duration, even after it is deleted by the user.
- Set retention rules to retain data for a specific period
- Set retention rules to delete data after a certain date
- Identify, preserve, and collect user data as a part of eDiscovery

To know more about what is Google Vault, Vault retention rules, holds, and license requirements, read our in-depth article.
1.2.3. Gmail retention using retention rules in Google Vault
Retain emails for a specific period: Organizations can configure retention rules in Google Vault to preserve relevant Gmail emails for a specific period. These emails will continue to be retained even when users delete the file.
Delete emails when no longer needed: Organizations can set retention rules to delete sensitive or unwanted emails from the user accounts and purge it from the Google systems.
- Default Retention Rules and
- Custom Retention Rules
Default retention rules
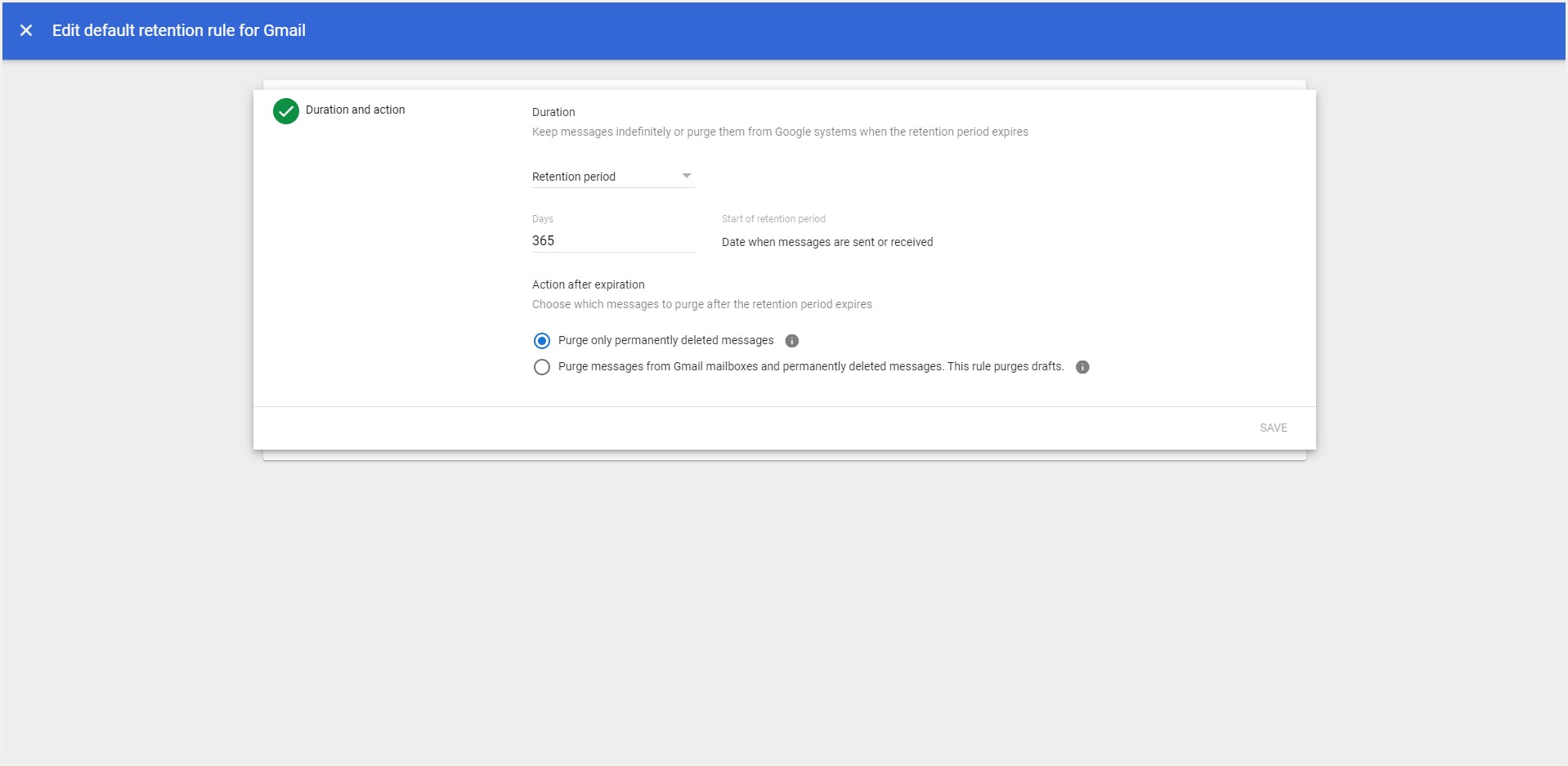
Custom retention rules
How to secure Gmail emails using retention rules?
Step 1: Sign-in to Google Vault using the Super Administrator credentials.
Step 2: Click “Retention”.
Step 3: Click “Custom Rules” from the navigation bar on top.
Step 4: Click “Create”.
Step 5: Select “Gmail” under the Service drop down, select the Scope (organizational units), add conditions if any (e.g.: sent date, subject line, username etc.), duration of the retention period, and action to be taken after the expiration of the policy.
Step 6: Click “CREATE”
What happens when a Gmail email gets deleted after applying a retention rule?
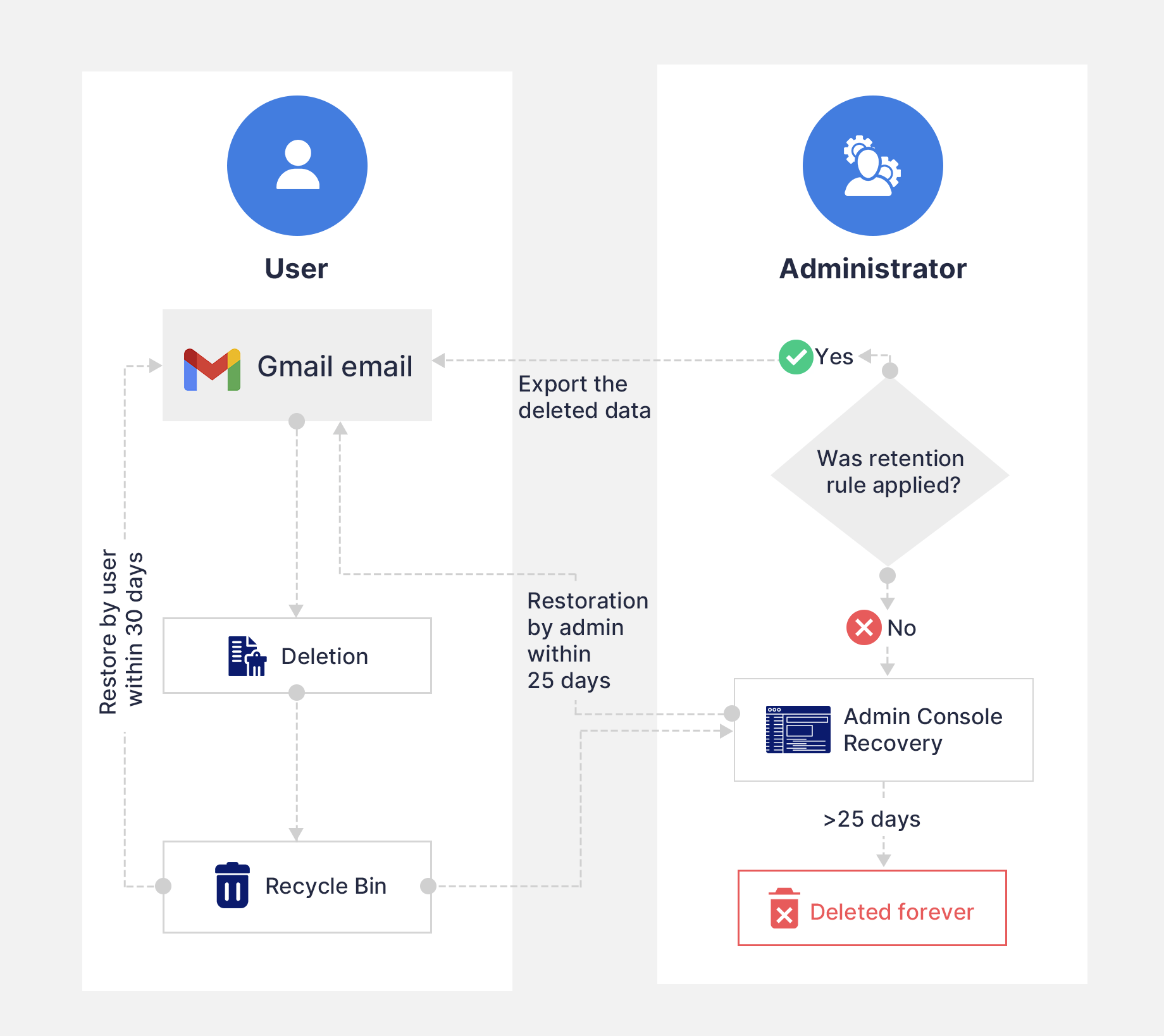
1.2.4. Gmail retention using eDiscovery in Google Vault
How to secure Gmail emails using eDiscovery?
Step 1: Sign-in to a Google Vault with Super Administrator credentials.
Step 2: Click “Matters”.
Step 3: Click “Create” or open an existing Matter.
Step 4: Click “HOLDS” from the top navigation bar.
Step 5: Click “Create”. Enter a name for the Hold,click “Gmail” under the Service drop-down. Choose a specific account or org units as the scope of the Hold,add conditions of the search (sent/received date, query terms).Click “CREATE”.
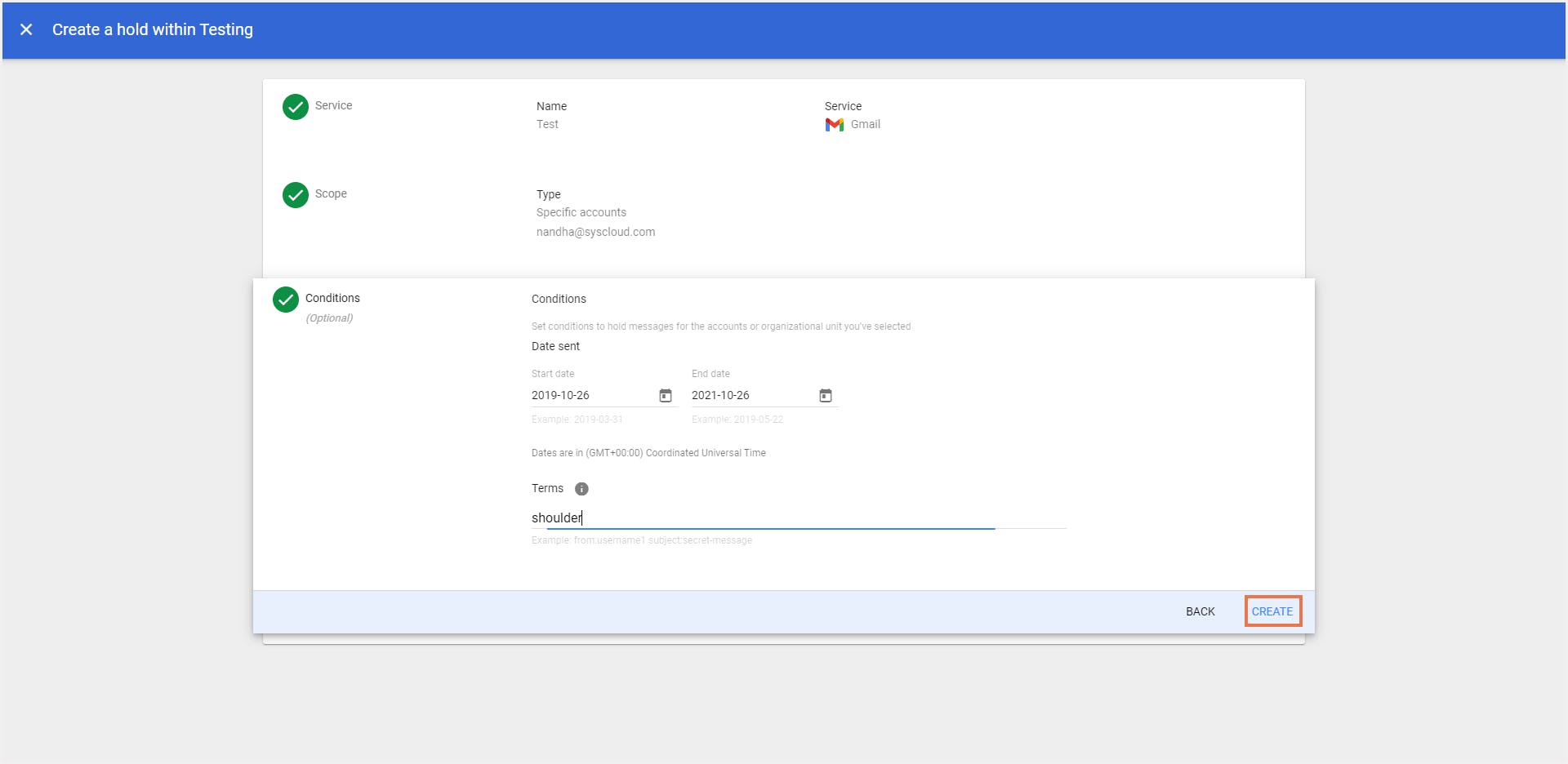
Can you delete emails that are put on eDiscovery hold in Google Workspace?
1.2.5. Can retention rules and eDiscovery holds be used as an alternative to cloud backup to secure Gmail emails?
Absence of restore Features- Unlike SysCloud, backup Google Vault does not help with data restoration at the click of a button. Additionally, SysCloud also allows organizations to restore individual emails and labels to a different user account (cross-user restore).
Deleted user accounts- If an administrator removes a Gmail user account in the organization’s Google Workspace domain, all emails related to that user is lost even if the account was placed on hold.
Comprehensive Backup- While Google Vault’s eDiscovery and retention rules help organizations preserve emails, it is not a backup solution. Third-party backup tools like SysCloud are capable of automatically backing up all Gmail data. SysCloud backup also provides the capability to export or restore the backed-up content with just a few clicks.
Outages- Gmail outages lock users out of important data for hours, impacting business productivity. Unlike eDiscovery holds, backup tools like SysCloud can help organizations access their files during outages and continue work during the downtime.
Click here to know more about SysCloud.
Recommended content
7 Dec 2021
11 min read
29 Nov 2021
12 min read
7 Dec 2021
10 min read
6 Dec 2021
15 min read
Get actionable SaaS administration insights
We don’t spam. Unsubscribe anytime.
In this article
- What is Gmail data retention?
- Default Gmail retention in Google Workspace
- Native Gmail retention settings
- Are retention rules and ediscovery an alternative to cloud backup?

