Categories
In this article
- Default Microsoft 365 retention
- Retention policy
- Legal holds
- Restrict accidental data deletion
- Limitations of native retention options
- Third - party cloud backup solutions
- What happens when Teams data is deleted
- SysCloud backup for Microsoft Teams
A Complete Guide to Microsoft Teams Retention
2 May 2024
8 min read
Anju George
Microsoft Teams is a collaborative workspace within Microsoft 365 that serves as a central hub for workplace conversations, teamwork, video chats, and document sharing. Due to the coronavirus pandemic and the resultant widespread adoption of a work-from-home model, there has been a dramatic increase in the number of Teams users over the past few years, rising to over 320 million users in 2024, making Teams the fastest-growing business app in Microsoft’s history.
Widespread adoption of Teams by businesses also means there is an increased risk of data loss for various reasons. Since Microsoft is not responsible for backing up your data, retaining Teams data is the responsibility of IT administrators so that business data is always available. This will come in handy during data loss and also ensure legal compliance.
To understand how retention works with Microsoft Teams, it is important to know where Microsoft Teams data is stored. Since Teams is a productivity hub that utilizes many applications and services across Microsoft 365, it stores data across multiple locations. To learn where the different types of data created or shared via Teams get stored, read our article A Guide to Teams Data Storage Location.
1. Default Microsoft 365 retention
1.1. Default Exchange retention
Items deleted from Exchange Online are moved to the Deleted Items folder where they remain for thirty days or until a user/admin empties it. When data is deleted from the Deleted Items folder, it is moved to the Recoverable Items folder where it is kept for 14 days (the period can be extended to 30 days via power shell) during which a user or an admin can restore it.
1.2. Default SharePoint retention
The data retained by default Microsoft retention is counted towards your Microsoft 365 storage quota, and you will need to purchase additional storage if you exceed the limit. Try SysCloud backup for Microsoft 365 to save on additional storage costs.
1.3. Limitations of default Microsoft 365 retention
- The data retained using the default retention is counted towards your Microsoft 365 storage quota, and you will need to purchase additional storage if you exceed the limit.
- Chat/channel messages aren't protected by standard Microsoft retention.
- Data is permanently deleted once the default retention period expires.
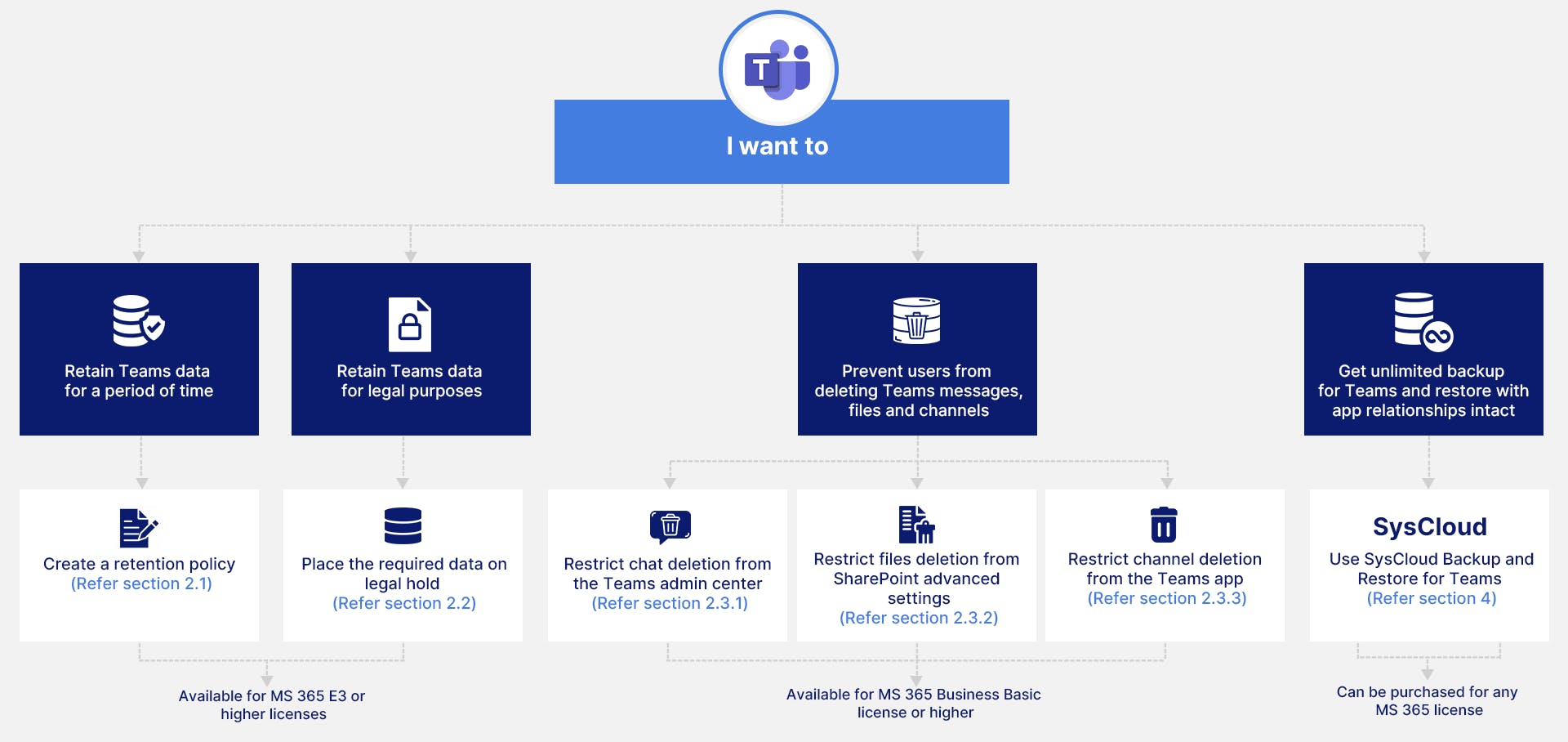
2. How can you retain Microsoft Teams data?
2.1. Retain Teams data using Teams retention policy
2.1.1. Introduction to Teams retention policy
2.1.2 Licensing requirements:
- Microsoft 365 E5/G5/A5/E3/G3/A3/F3/F1, Business Basic, Business Standard, and Business Premium
- Office 365 E5/G5/A5/E3/G3/A3/F3/E1/G1
- Microsoft 365 F5 Compliance and Microsoft 365 F5 Security and Compliance add-on plans
Learn more about Microsoft 365 licensing requirements for retention policies.
2.1.3. Retention policy for Teams chat and channel messages
2.1.3.1. How to create a Microsoft Teams retention policy for chat and channel messages
Note: To create and configure retention policies, one needs to be a global admin or a compliance admin.
Step 1: Open the Compliance admin center (now Microsoft Purview compliance portal) and navigate to the Solutions section.
Step 2: Select Data lifecycle management -> Microsoft 365 and navigate to the Retention policies tab. Click New retention policy to start the Create retention policy configuration.

Step 3: Enter a name and description (optional) for your new retention policy.
Step 4: For the Choose the type of retention policy to create page, select Adaptive or Static.

Decide whether it will be adaptive or static before you create your retention policy. For more information, see Adaptive or static policy scopes for retention.
If you choose to create an adaptive policy, you must create one or more adaptive scopes before setting up your retention policy. If you haven't already created adaptive scopes, you can still select Adaptive but since there won't be any adaptive scopes to choose from, you won't be able to finish the configuration with this option. To learn more about configuring adaptive scopes, see Configuration information for adaptive scopes.
Step 5: Depending on the scope you selected:
If you chose Adaptive: On the Choose adaptive policy scopes and locations page, click Add scopes and choose one or more from the previously created adaptive scopes. Then, select one or more locations. The locations you can choose will depend on the scope types you have added. For example, if you added only a scope type of User, you can select Teams chats but not Teams channel messages.
If you chose Static: On the Choose locations to apply the policy page, choose one or more locations for Teams:
-Teams channel message: This includes messages from standard and shared channel chats, and standard and shared channel meetings, but excludes private channels that have their own policy location.
-Teams chats and Copilot interactions: For Teams, this covers messages from private 1:1 chats, group chats, meeting chats, and chat with yourself. For Copilot for Microsoft 365, it includes all user prompts to Copilot and Copilot's responses.
-Teams private channel messages: This option includes messages from private channel chats and private channel meetings. If you choose his option, you can't select other Teams locations in the same retention policy.
You also have the option to include/exclude specific teams or users. By default, all teams and all users are selected, but you can refine this by selecting the Choose and Exclude options.

Note: Teams private channel messages location has to be selected separately and cannot be chosen in the same policy as the other two locations.
Step 6: For Decide if you want to retain content, delete it, or both page, specify the retention settings based on your organization's requirements.
To learn more, see Settings for retaining and deleting content.

Step 7: Review the settings and click Submit. Your new retention policy will be created.
Refer to this Microsoft documentation for technical details about how retention works for Teams, including what elements of messages are supported for retention and timing details with illustrative examples.
2.1.3.2. How retention works with Teams chat and channel messages
If you configure a Teams retention policy to retain chats or channel messages, users can still edit/delete messages within the Teams app. They can no longer see their pre-edited or deleted messages within the Teams app but a copy of these messages is retained in a secure location that's designed for eDiscovery searches by compliance administrators. (Learn more about the different locations in which Teams data get stored) Permanent deletion of chat/channel data doesn’t happen before the end of the configured retention period.
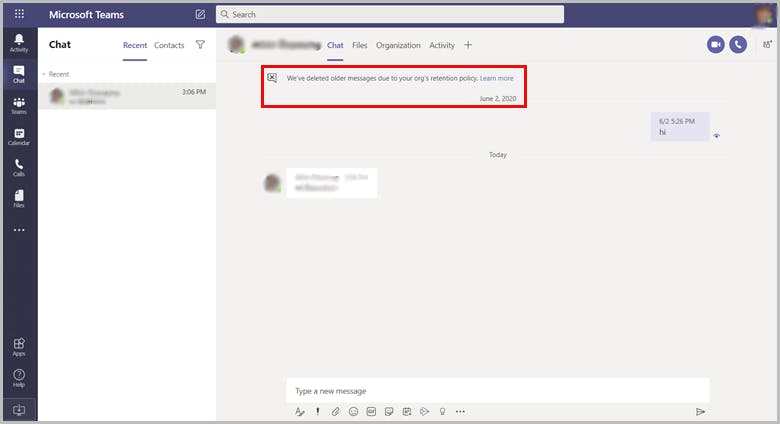
For private chats or group chats: Messages older than the retention policy configuration are deleted with an automatically generated message stating "We've deleted older messages due to your org's retention policy" shown on top of yet undeleted messages.
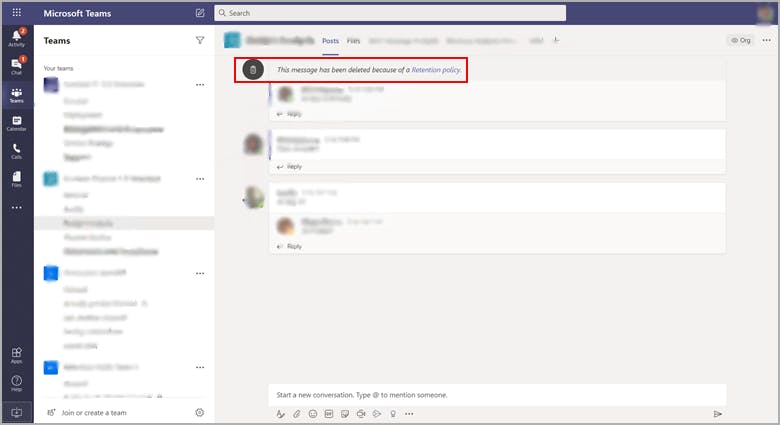
For channel messages: Messages older than the retention policy configuration are deleted. If the deleted message was a parent message of a threaded conversation, a message stating “This message has been deleted because of a Retention Policy” will be displayed in place of the parent message. All replies in the thread which are still within the retention period will remain.
If the messages that were previously subject to a retain action are now deleted/edited by users within the app, these messages will be deleted from the secured location and no longer accessible via eDiscovery searches. For more information on how retention works for Teams chat and channel messages, click here.
2.1.4. Retention policy for files shared in Teams
To better understand which SharePoint sites and OneDrive accounts need to be selected for applying the retention policy, you need to know where the files shared within Teams are stored. Read our detailed article on Teams data storage location to learn where the different types of Teams data get stored.
Retained files are stored in the Preservation Hold Library, and data in the Preservation Hold Library counts against your SharePoint storage quota. The total SharePoint storage limit per organization is set at 1TB plus 10GB x number of licensed Microsoft 365 users in your tenant. If you exceed the limit, you will have to purchase additional storage priced at $200/month/TB. (The cost and availability of additional storage may vary based on your specific Microsoft 365 licensing agreement and the region. It's a good practice to verify the current pricing directly through your Microsoft 365 admin center or contact Microsoft support for the most accurate and tailored pricing information.)
To save on storage costs, you can opt for a third-party cloud backup solution, like SysCloud.
How to create a retention policy for Teams files
Step 1: Open the Compliance admin center (now Microsoft Purview compliance portal) and navigate to the Solutions section.
Step 2: Select Data lifecycle management -> Microsoft 365 and navigate to the Retention policies tab. Click New retention policy to start the Create retention policy configuration.
Step 3: Enter a name and description (optional) for your new retention policy.

Step 4: For the Choose the type of retention policy to create page, select Adaptive or Static.
Step 5: Depending on the scope you selected:
If you chose Adaptive: On the Choose adaptive policy scopes and locations page, click Add scopes and choose one or more from the previously created adaptive scopes. Then, select one or more locations. The locations you can choose will depend on the scope types you have added.
If you chose Static: On the Choose locations to apply the policy page, select the SharePoint sites and(or) OneDrive accounts corresponding to the channel and(or) chat files you want to retain respectively.

Step 6: For Decide if you want to retain content, delete it, or both page, specify the retention settings based on your organization's requirements.
Step 7: Review the settings and click Submit. Your new retention policy will be created.
Note: If you have a retention policy that deletes a file shared via a Teams chat or channel message before the message is deleted, the file will continue to show up in the Teams message. However, if you click on the file you’ll receive a “File not found” error. You could also receive this error if someone were to manually delete the file from SharePoint Online or OneDrive for Business with no retention policy in place.
To learn more on how retention policy works for SharePoint, read this article.
2.1.5. Retention policy for Teams data stored in Exchange Online
Except for Microsoft Teams chat and channel messages, Teams data stored in Exchange Online such as Calendar data and group emails must be retained using Exchange Online retention policy. (Since Teams retention policy only covers chat and channel messages) To learn more about where different types of data within Teams are stored, read our article: A Guide to Microsoft Teams Data Storage Location
Click here to learn more about retention for Exchange Online data.
2.1.6. Retention policy for Teams created from Microsoft Groups
How to create a Groups retention policy
Step 1: Open the Compliance admin center (now Microsoft Purview compliance portal) and navigate to the Solutions section.
Step 2: Select Data lifecycle management -> Microsoft 365 and navigate to the Retention policies tab. Click New retention policy to start the Create retention policy configuration.
Step 3: Enter a name and description (optional) for your new retention policy.

Step 4: For the Choose the type of retention policy to create page, select Adaptive or Static.
Step 5: Depending on the scope you selected:
If you chose Adaptive: On the Choose adaptive policy scopes and locations page, click Add scopes and choose one or more from the previously created adaptive scopes. Then, select one or more locations. The locations you can choose will depend on the scope types you have added.
If you chose Static: On the Choose locations to apply the policy page, select the Microsoft 365 groups corresponding to the teams you want to retain.

Step 6: For Decide if you want to retain content, delete it, or both page, specify the retention settings based on your organization's requirements.
Step 7: Review the settings and click Submit. Your new retention policy will be created.
A retention policy applied to a Microsoft 365 group will include the group's mailbox and the connected SharePoint team site by default. However, you can customize this setting using the Set-RetentionCompliancePolicy PowerShell cmdlet.
To specify that the retention policy should apply only to the group's Microsoft 365 mailboxes, you would use the parameter Group:Exchange.
Conversely, if you want the policy to apply only to the SharePoint sites connected to the group, you would use Group:SharePoint. If you wish to revert to the default setting where the policy applies to both the mailbox and SharePoint site, you can use Group:Exchange,SharePoint.
To learn more about retention policies and how they differ from retention labels, read our article Microsoft 365 Retention Policy and Retention Label: A Complete Guide
Quiz time! Which of the following helps you back up your data?
2.2. Retain Teams data using legal holds
This legal hold ensures that even if a message is modified or deleted within Teams, a copy of the original message is preserved and discoverable via eDiscovery tools. This includes private channel chats stored in the individual user mailboxes and standard channel chats stored in the mailbox associated with the parent team. Files shared in channels, stored in the team's SharePoint site are also covered under the legal hold. (See Content locations to place on hold to preserve Teams content)
Read this article to learn more about legal holds and how to place Teams data on hold.
2.3. Restricting accidental deletion by users
2.3.1. How to restrict chat deletion from the Microsoft Teams Admin Center
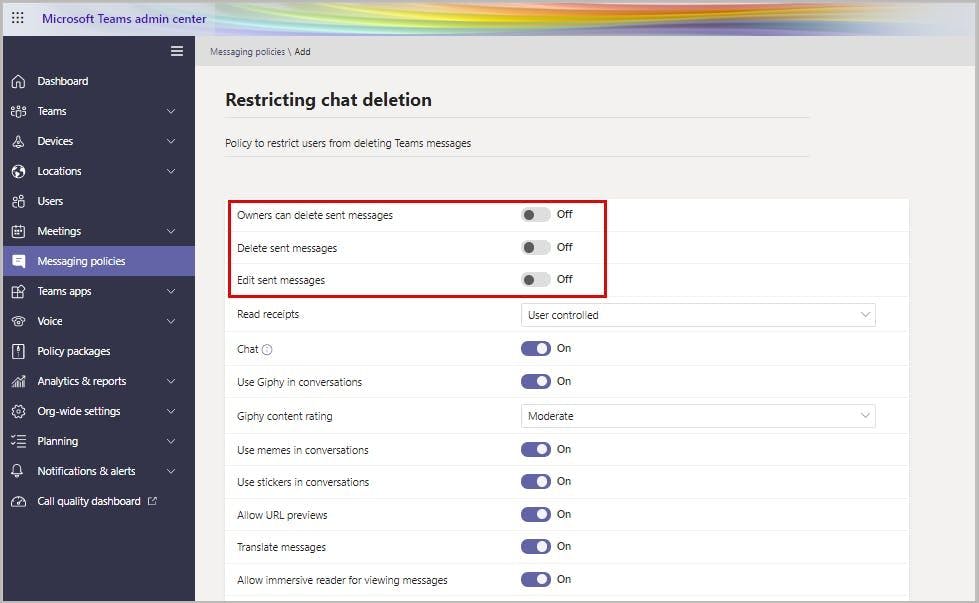
Step 1: Go to the Teams admin center. Navigate to Messaging policies and click on the +Add button.
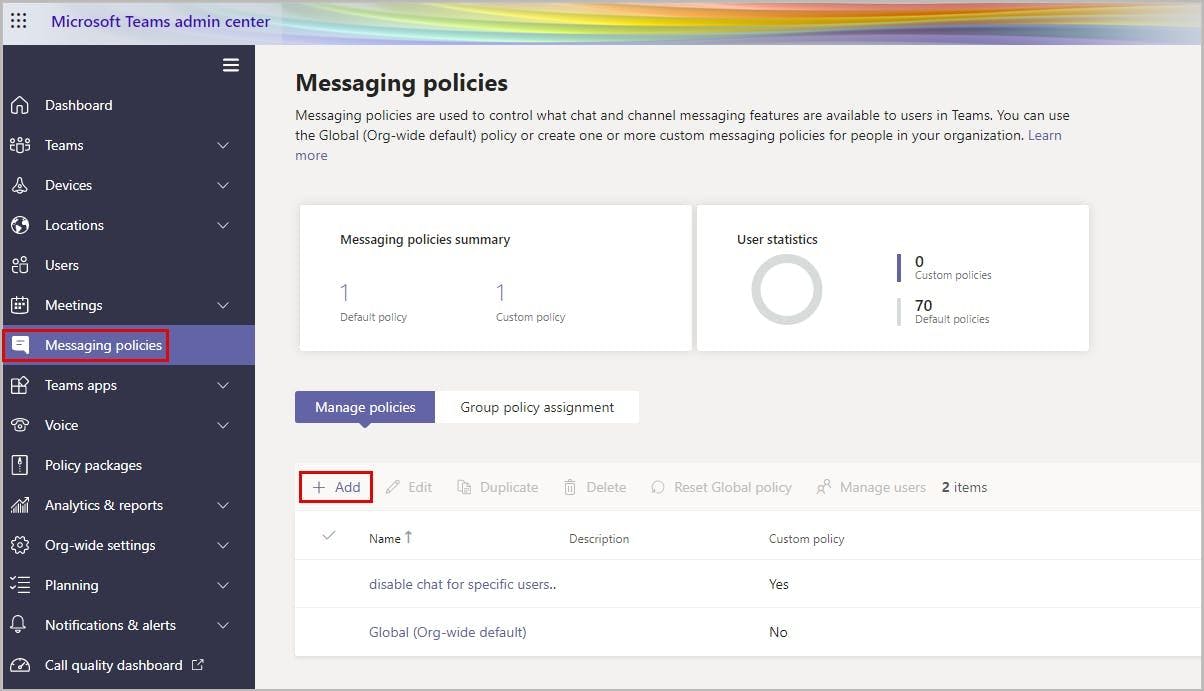
Step 2: Disable the policies Owners can delete sent messages and Delete sent messages. You can also disable Edit sent messages policy if you don’t want users to edit sent messages. Click Save.
2.3.2. How to restrict files deletion using SharePoint advanced settings
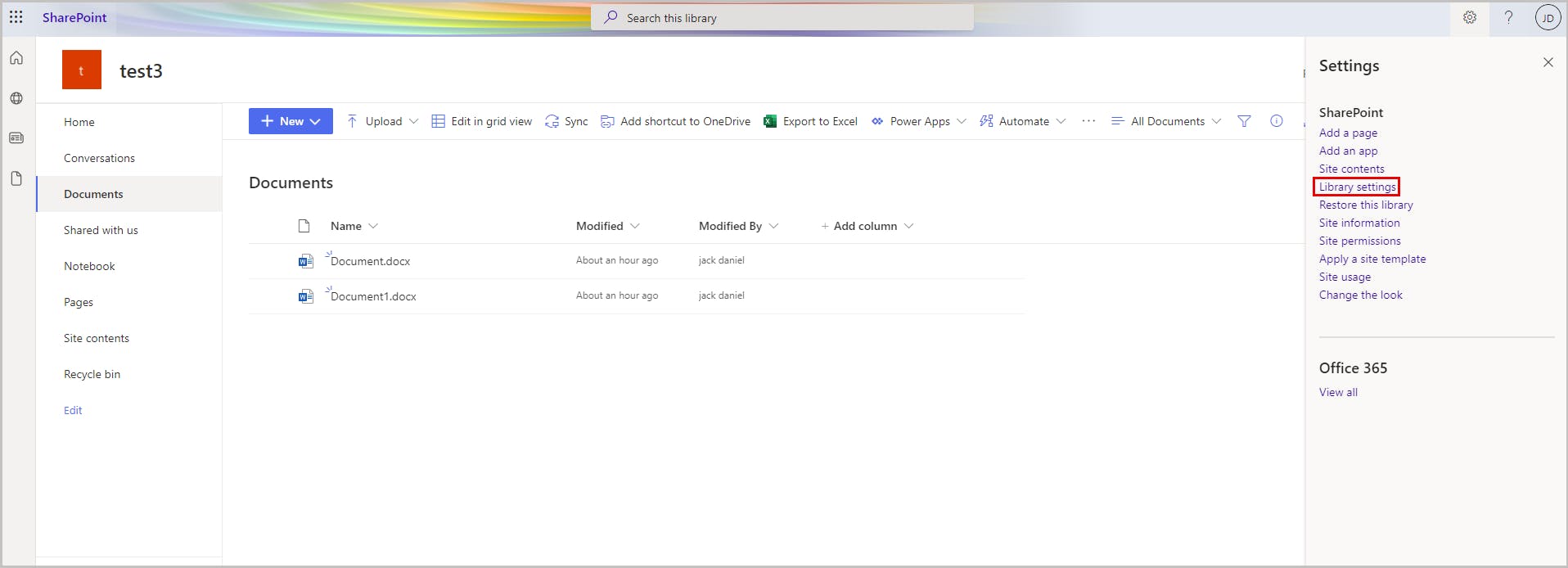
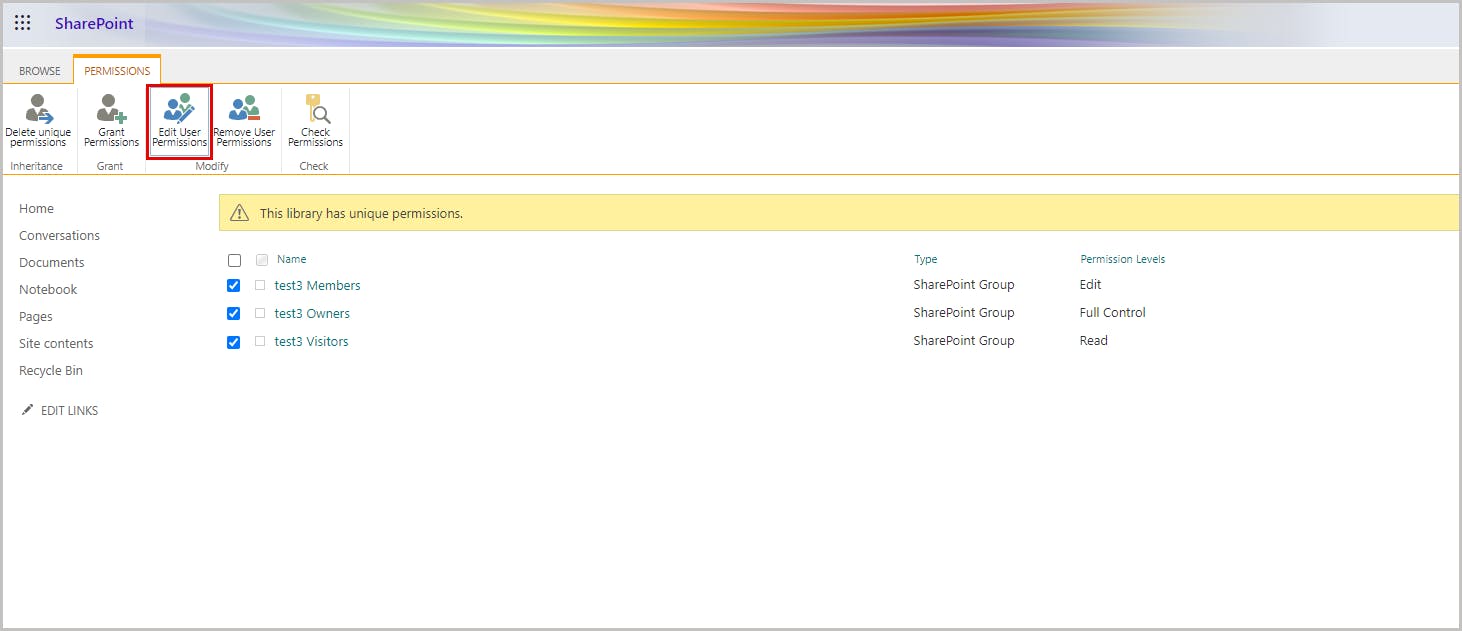
Step 1: Open the SharePoint document library for which you want to edit user permissions.
Step 2: Click the gear icon and select Library settings.
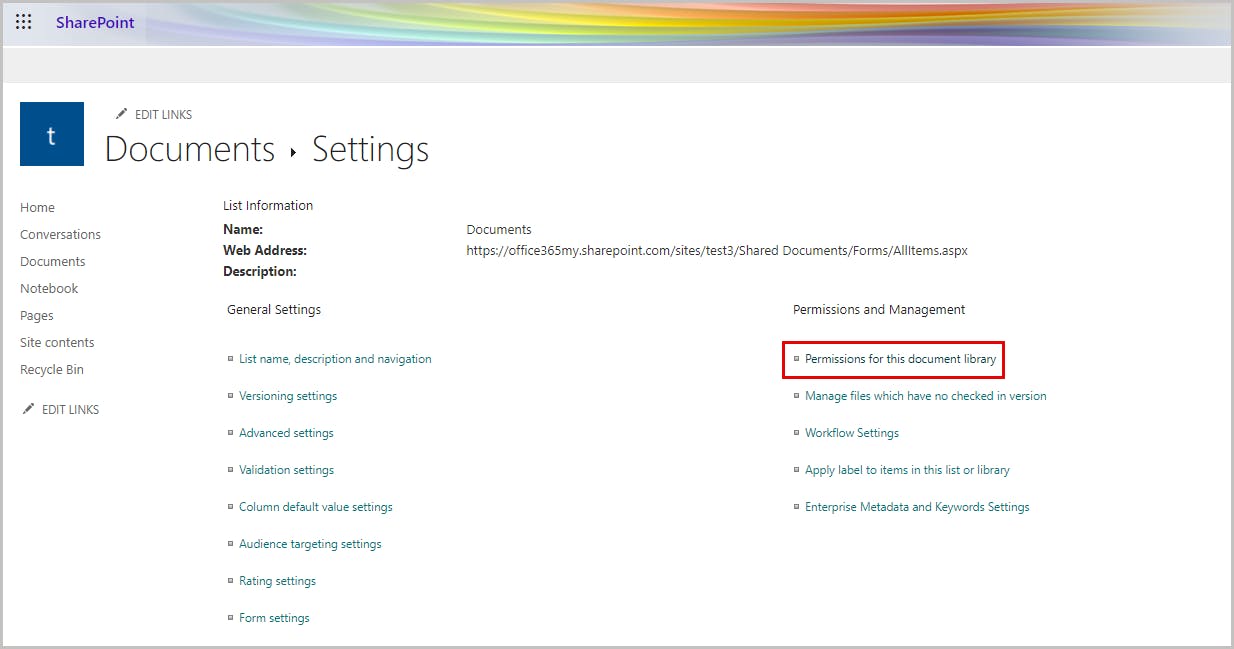
Step 3: Under Permissions and Management, select Permissions for this document library.
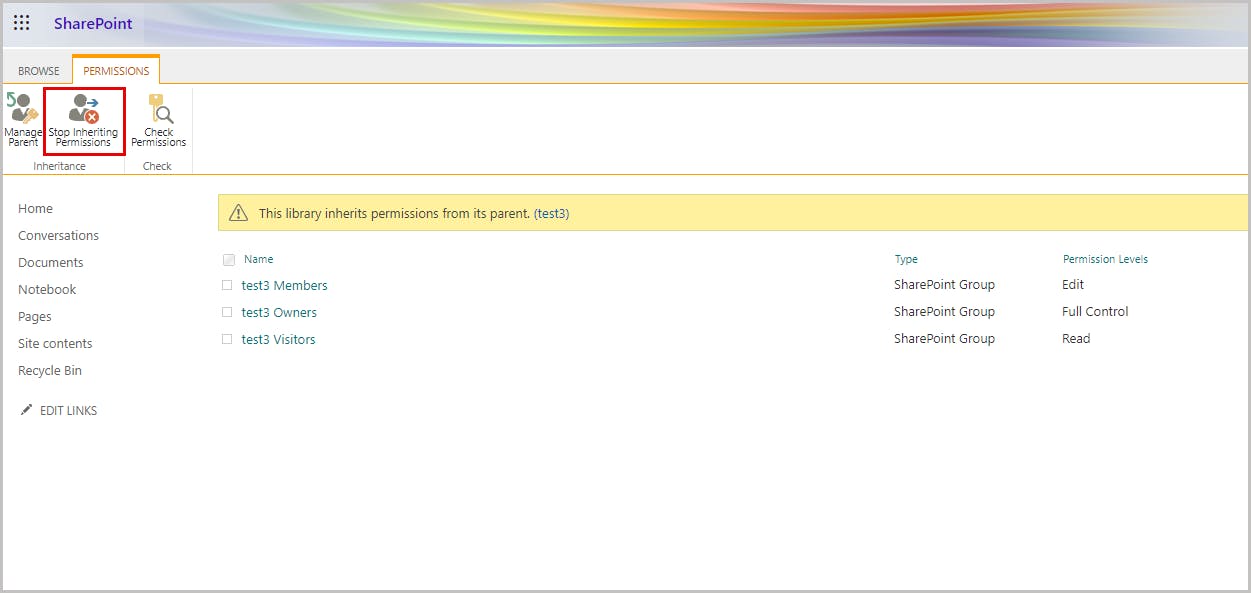
Step 4: Select Stop Inheriting Permissions to prevent users from inheriting the permissions of the parent site.
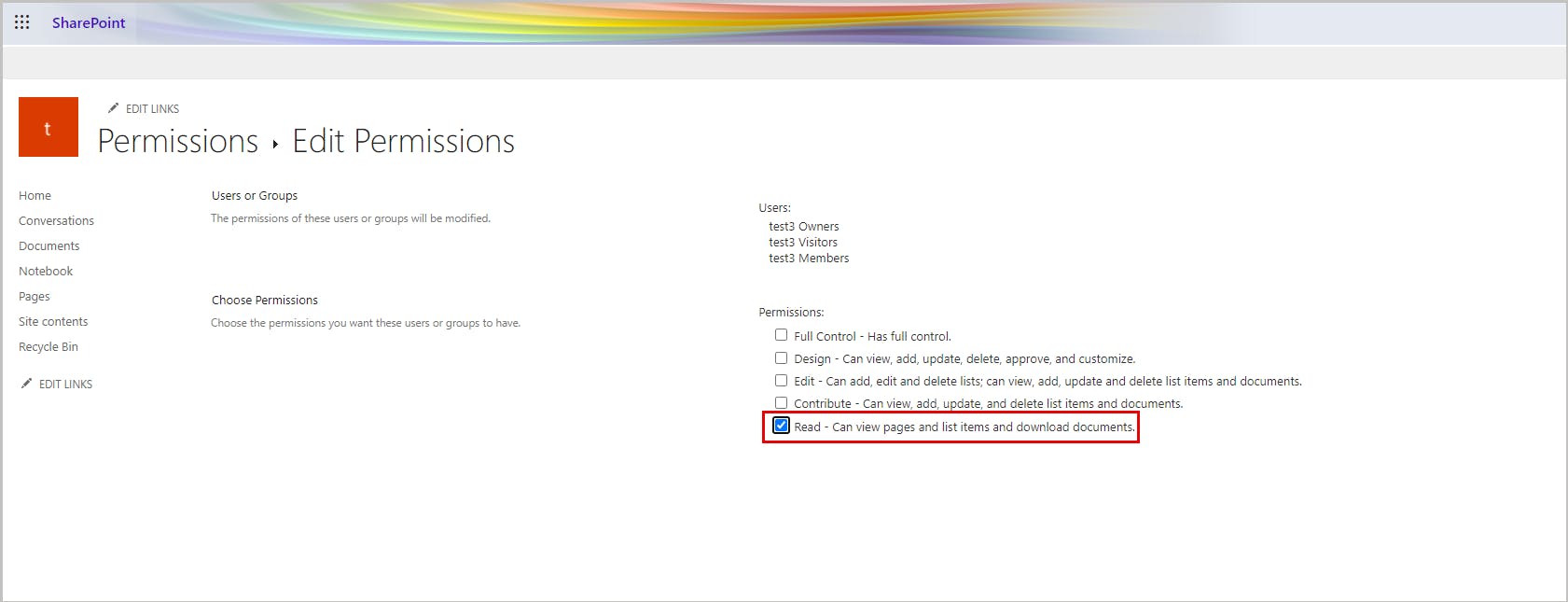
Step 5: Go to Edit User Permissions. To prevent users from deleting Teams files, change the permission to Read.
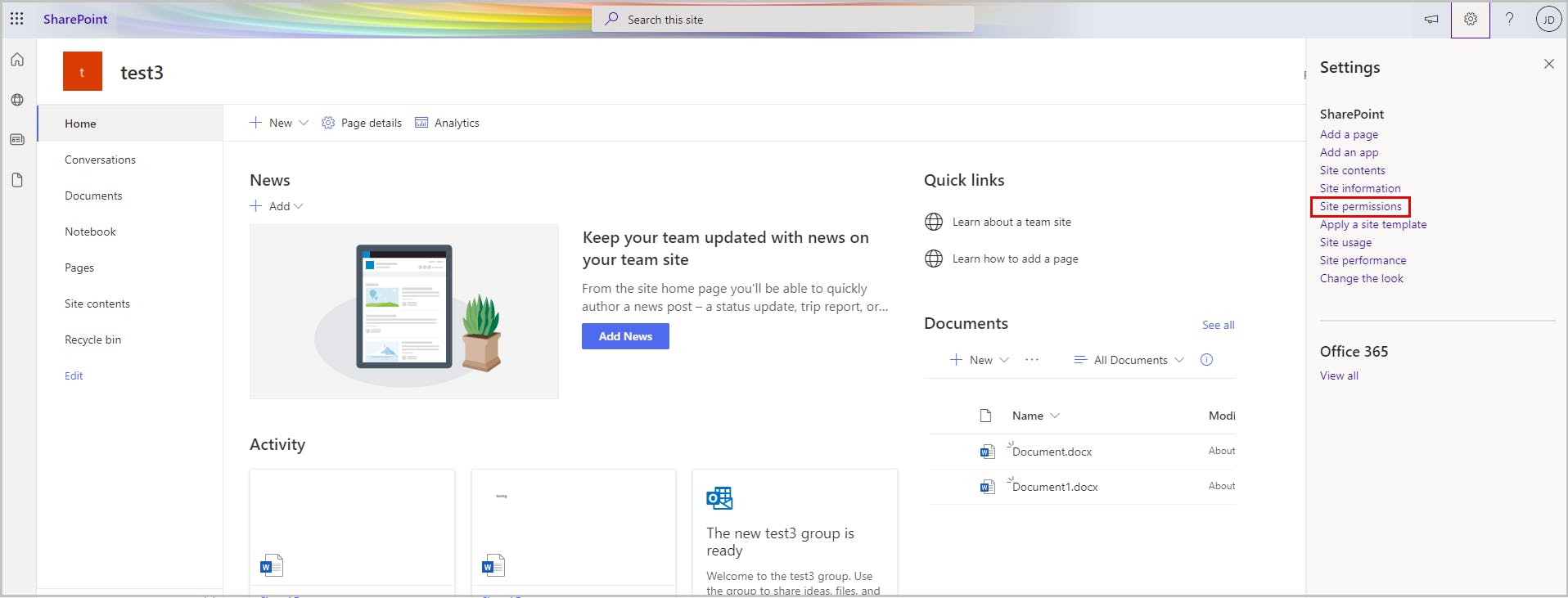
You can also edit the user permissions for the whole site instead of a document library. To do this, open the team site -> click the gear icon -> Site permissions -> Advanced permission settings, and follow the rest of the steps mentioned before.
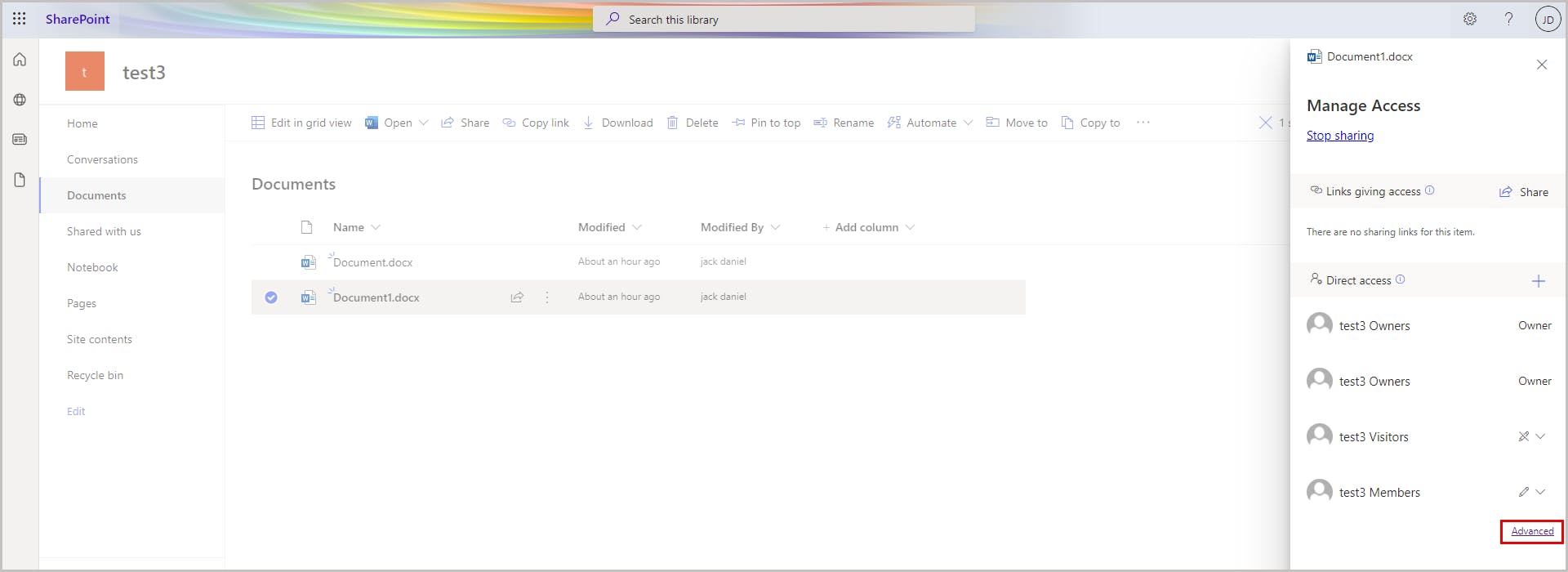
You can also edit the user permissions for specific files. To do this, right-click the required file -> Manage access -> Advanced, and follow the rest of the steps mentioned above.
2.3.3. How to restrict channel deletion from the Teams application
Note: You need to be a team owner to perform this.
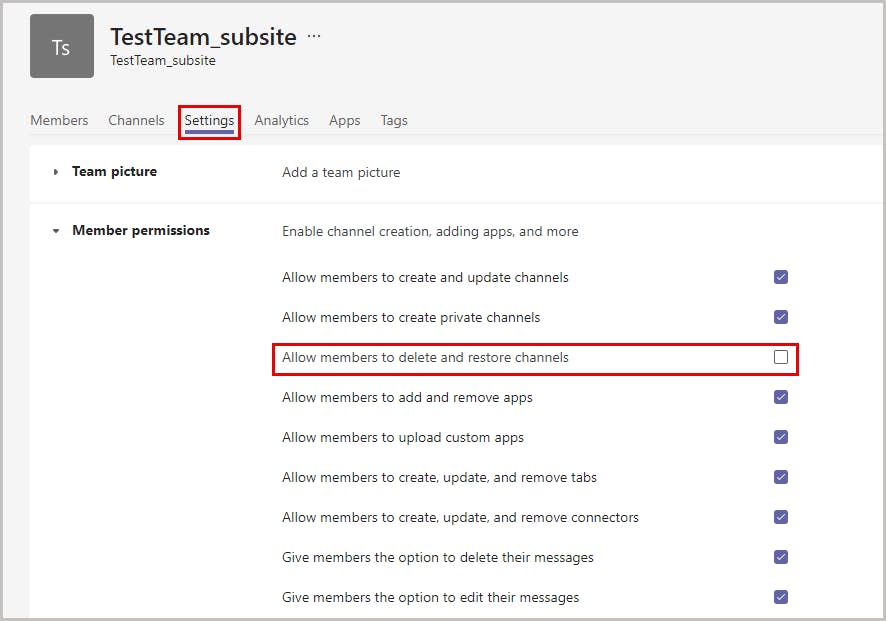
Step 1: In the Teams application, click the three dotted lines next to the team name, then choose Manage team from the drop-down menu.
Step 2: Navigate to Settings. (This tab will only be visible to the team owners.) Under Member permissions, uncheck the option Allow members to delete and restore channels.
2.4 Limitations of native Teams data retention options
- Retained Teams data counts towards your Microsoft 365 storage quota. Each user has limited storage available. If you delete data to stay within storage limits, such data cannot be recovered. Because Microsoft retains full versions of all deleted and modified data (without providing incremental backups), Microsoft 365 storage limits can be reached quickly.
- Unlike third-party backup tools, native retention methods lack automated recovery features. In the event of data loss, retained data can only be exported offline and restored manually. Restoring a large amount of data will require manual effort and time.
- Retention policies and legal holds are part of the Microsoft Purview compliance portal which is only available in senior E3/E5 plans that are more expensive than Microsoft (Office) 365 Business plans.
- If a Microsoft 365 account is compromised by a ransomware attack, resulting in data encryption, all data covered under native Microsoft retention could also be encrypted. Thus, maintaining regular backups in a separate environment is crucial for effective data recovery
2.5 Retain Teams data using third - party cloud backup solutions
Third-party cloud backup solutions like SysCloud can be used to back up and restore your Microsoft Teams data effortlessly. SysCloud Microsoft 365 backup allows admins to back up Teams channel conversations and files, and export or restore them whenever needed.
Learn more about SysCloud backup for Microsoft Teams
2.5.1. Why should you use third-party cloud backup tools to back up Microsoft Teams?
The following are the advantages of using third-party cloud backup tools like SysCloud to backup your Teams data:
Save licensing costs: Keep a safe copy of Teams data even after the user accounts are deleted. This happens mostly during employee exits, thus saving on license costs.
Access data during outages: Access your Teams data via the SysCloud backup app even when Microsoft 365 suffers an outage, which is very common.
Added security: Gain added data security with increased admin control and built-in protection for ransomware attacks.
Regular activity reports: Get granular reports of all the activities in the backup account.
AI-powered copilot: Efficiently manage backups, troubleshoot errors, and access data through a chat interface.
Customizable: Customize to fit the unique backup and restore needs of any organization.
3. What happens when Teams data is deleted
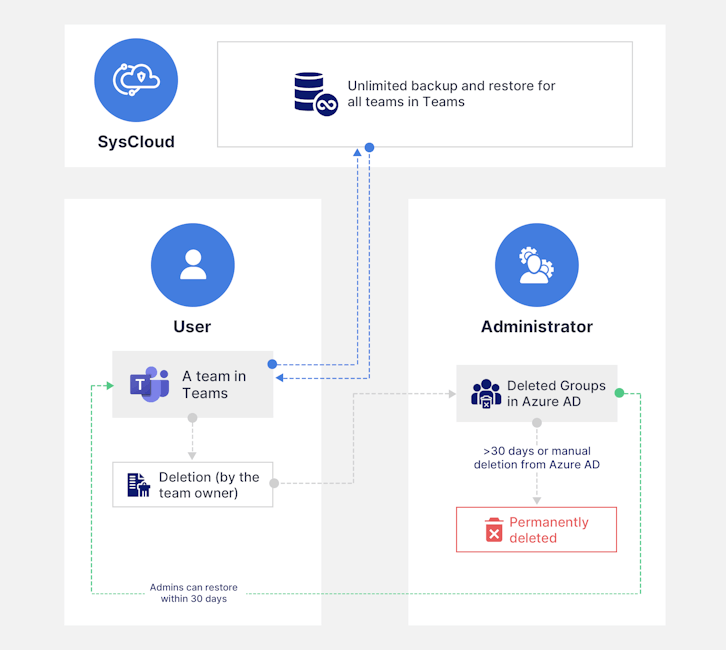
3.1 If an entire team is deleted:
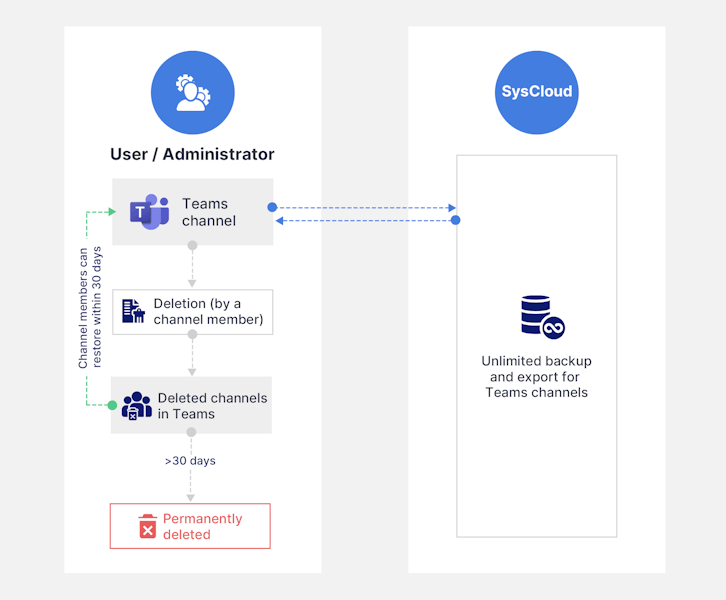
3.2. If a Teams channel is deleted:
If the Allow members to delete and restore channels option under Member permissions in the team settings is checked, any member of the team can restore the deleted channel by going to Manage team > Channels > Deleted. For detailed steps on recovering deleted Teams data, refer to our in-depth guide: How to Recover Deleted Teams Data
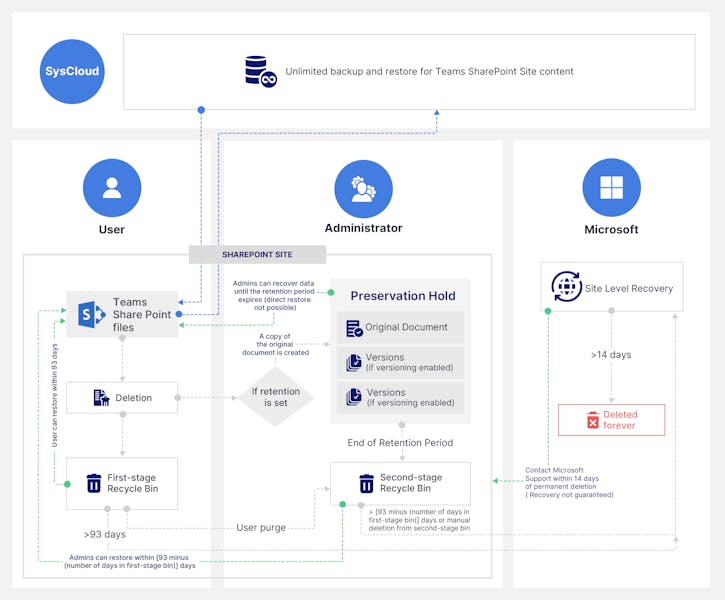
3.3 If Teams SharePoint files are deleted:
Without retention: On deletion, Teams data stored in SharePoint moves to the first-stage Recycle Bin (site Recycle Bin) where it remains for 93 days unless someone deletes it from there. In that case, the data moves to the second-stage Recycle Bin (site collection Recycle Bin) where it stays for the remainder of the 93 days, before getting permanently deleted. The administrator can contact Microsoft support within 14 days of deletion (from the second-stage Recycle Bin) for a site-level recovery, but restore is not always guaranteed.
With retention: If a retention policy is in place, a copy of the original data will be created in the Preservation Hold Library, where it stays until the end of the retention period. Once the retention period expires, the data moves to the second-stage Recycle Bin, and is permanently deleted at the end of 93 days. The administrator can contact Microsoft support within 14 days of deletion (from the second-stage Recycle Bin) for a site-level recovery, but restore is not always guaranteed. Learn more.
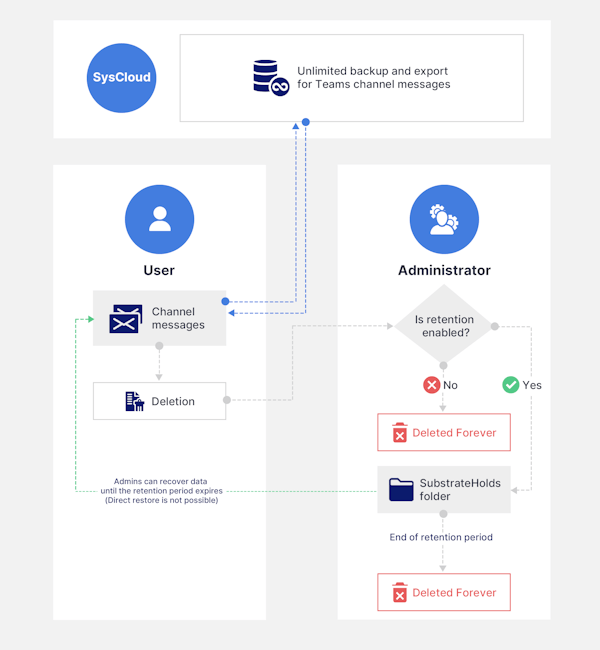
3.4 If Teams channel messages are deleted:
Without retention: When you delete channel messages, they are permanently deleted and cannot be recovered by anyone unless retention has been enabled for Teams channel messages.
With retention: The original copy of the Teams message is preserved in a hidden folder in Exchange Online, called the SubstrateHolds folder (part of the Recoverable Items folder), where they remain until the retention period expires. Once the retention period expires, these messages are permanently deleted.
To know how to recover deleted Teams data, read our article How to Recover Deleted Teams Data.
4. SysCloud backup for Microsoft Teams
Using SysCloud, administrators can back up Microsoft Teams and the native Microsoft 365 apps connected to the team. Both public and private teams can be backed up with SysCloud. Admins can back up specific teams whenever required (using the On-demand backup feature) or enable the Auto backup feature to back up new teams automatically.


4.1. SysCloud Microsoft Teams backup features
Make smarter backups: Automate backups for Teams sites, channels, and conversations, and files from other Microsoft 365 apps connected to channels.

Advanced restore options: Restore teams, channels and files from any point-in-time with in-app relationships intact.

Export posts at the channel level: Instantly export private and public channel conversations.

Maintain a clean backup copy: Proactively monitor and manage data backed up for ransomware alerts and compliance gaps with SysCloud’s intelligent backup data insights.

4.2 SysCloud Teams backup vs. native Microsoft retention settings
| Features | SysCloud | Native Microsoft Retention Settings | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Backup Teams Channel conversations | |||||
Backup Teams Site content: Subsites, Site pages, OneNote, Lists, Document library | |||||
Export Teams posts at a channel level | |||||
Show more | |||||
Learn more about SysCloud backup for Microsoft Teams.
Recommended content
11 May 2023
2 min read
3 May 2023
3 min read
12 Jun 2024
8 min read
Get actionable SaaS administration insights
We don’t spam. Unsubscribe anytime.
In this article
- Default Microsoft 365 retention
- Retention policy
- Legal holds
- Restrict accidental data deletion
- Limitations of native retention options
- Third - party cloud backup solutions
- What happens when Teams data is deleted
- SysCloud backup for Microsoft Teams

